Part 2: Cloud Computing – A Complex Ecosystem?
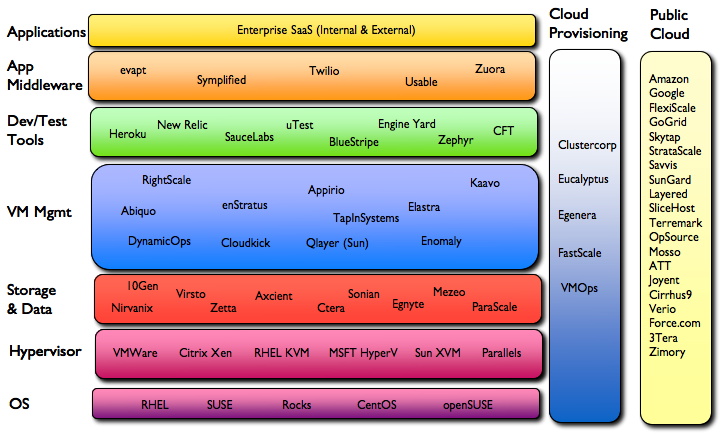
There are many different ways to categorize the players involved in enabling the Cloud Computing space. A simple category consists of those who simply provide “Public Cloud” services – 3rd parties who host the services for enterprises outside the fire-wall.
Then there’s a small group who help you provision cloud services (private and/or public) from “bare metal” (starting with the actual hardware). These companies will attempt to install the software on your datacenter servers from operating system to enterprise applications.
Lastly, there’s the cloud stack itself – the software that makes up the software components used by enterprises to deploy public and private cloud services.
- Public Cloud Vendors
- Cloud Provisioning
- Cloud Stack
Enterprise Applications
These applications can consist of legacy programs developed for departments within enterprise lines of business, whether they be executive tools in general, marketing, sales, engineering, HR, finance, manufacturing, or otherwise.
Application Middleware
These applications are components of the cloud offering that tightly integrate with enterprise application layer, often augmenting it. Examples include:
- Monetization/Billing/Payments
- Identity/authentication
- Voice
Development & Test
These applications are used to help develop and debug cloud applications – namely, a development environment. Examples include:
- Ruby on Rails dev platform
- Virtual machine application stack creation/test
- Quality Assurance
Virtualization Management
This suite of applications provide value-add on top of public cloud providers (e.g. Amazon) with extended management dashboards as well as hypervisor console extensions. Example functionality includes:
- Virtual machine deployment, monitoring, bundling
- Image configuration, tracking, modification (within VM)
- User access controls
- Load balancing / auto-scaling
- Application frameworks (e.g. for force.com, google, etc.)
- Hierarchy navigation (cloud -> datacenter -> rack -> physical box -> VMs)
Cloud storage / data management
This segment can provided as a part of a storage-centric public cloud service or as components to building your private cloud. Functionality includes:
- Create & manage cloud storage
- Virtualization of server storage
- Storage SaaS
- HW solutions for Cloud attached storage
- On-demand file serving
- Data security
Provisioning Systems
These systems are the most complex, offering to automate the creation of datacenter cloud installations (whether for private or public usage). Functionality can include:
- Bare metal provisioning (to VM layer) for Private Clouds
- VM application stack provisioning (Private & Public)
- Private/Public cloud software upgrades/lifecycle management
- API layer mimicking public cloud service, providing seamless private/public cloud application I/F
Public Cloud Offerings
A host of providers fit into this space, with the top ten players including:
- Amazon EC2
- DAAS.com
- Flexiscale
- Joyent Accelerators
- Microsoft Azure
- Rackspace Mosso Cloud
- ServePath GoGrid
- Skytap
- Sun Microsystems Cloud
- Terremark Enterprise Cloud


3 thoughts on “Part 2: Cloud Computing – A Complex Ecosystem?”
Comments are closed.